A Typical Transactional database schema
Below is a typical schema diagram from a transactional DBMS. As you can see this is a complex design and is not appropriate for extracting large amounts of data for Management Information (MI) purposes. It typically requires expert knowledge from the application designer. Any MI analysis type queries executed against a transactional DBMS are likely to be complex and slow. You would not want to present this schema to business stakeholders to query on an ad-hoc basis.

A Typical Data Warehouse Schema
When we build Data Warehouses and Data Marts we vastly simplify transactional schemas to create a Data Warehouse schema like the one below. Data is cleansed and summarised to present a simpler view of the same data that is easy for business stakeholders to understand and is capable of returning large data sets as quickly as possible.
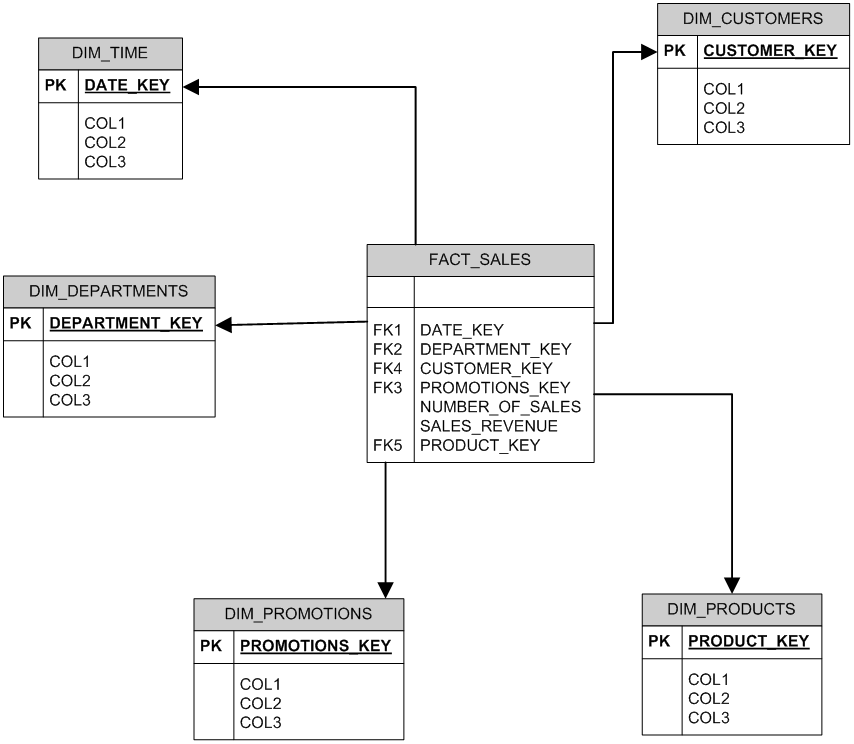
This is also known as a star schema. In a star schema all data about each entity is gathered together and presented as a single entity.
Implementing a Data Warehouse
Like any project requirements need to be gathered with Analysis, Design, Implementation and Testing phases.
Design phase – Typically Data Warehouses are populated daily by an overnight batch process. This is a three stage process known as ETL –
- Extract – Fetch the data from all source databases and place in a data staging area of the data warehouse database.
- Transform – Code routines which brings together the staged source data, removing errors, formatting, simplifying and summarizing the data.
- Load – Populate the data warehouse tables.
Once the ETL has been designed. A business intelligence tool need to be configured to point at the final data warehouse tables. Report templates to allow easy ad-hoc reporting need to be provided using the BI tool. Once this is complete some basic training needs to be provided to get users familiar with the new reporting capabilities. Developing a group of power users is also a good idea.

Ideally in a data warehouse batch process, we want to fetch only the data that has changed from the previous day plus records that have been added as new. Can be slow and inefficient to capture an entire table daily when we will only be processing the latest records.
Data from Presentation Area usually copied to separate read-only database which is where user report are executed against. Sometimes the Data Presentation area is split into separate databases based on department or a business function. These are known as Data Marts.
Data Cleansing Example
Here is an example of cleansing customer data. Data could be coming from a single or multiple sources. In a data warehouse we ideally need to produce a single unique list of customers.
ETL tools currently on the market include built in tools and algorithms to “fuzzy match” the records below to produce a single record for that customer. A huge time saver but results will never be 100%.

Data Warehouse ETL Tools
There are currently a wide variety of ETL tools on the market –
- Oracle Warehouse Builder
- Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services
- Business Objects Data Integrator (SAP)
- SAS Data Integration Studio
- Informatica Powercenter
- IBM Information Center
- Script ETL code routines by hand.
The above tools fall into three categories – Database Integrated, BI Integrated or Pure ETL tools. Other niche ETL tools are also available. Hand cut code can mean a long delivery time. Could be cheaper as you don’t have to invest in licenses for ETL tools. However it could be higher maintenance. Difficult to see overall picture of the Data Warehouse batch. ETL Tools need an investment at the outset. Cheaper and easier to maintain your data warehouse batch.
Data Warehouse Trends
Rather than a single overnight batch process, database vendors such as Oracle are now providing the capability to “drip-feed” data from the live operational database to the Data Warehouse database. This will mean the DW database will be populated with the latest data throughout the day giving operational reporting capabilities that managers crave.
Data Mining – Techniques and software algorithms used to spot hidden trends and patterns in your data. (e.g. Oracle Data Miner).
Business Intelligence Tools
Hand in hand with data warehouses is the use of Business Intelligence (BI) tools to query the data warehouse. BI often referred to as decision support systems.
- Application software designed to report, analyze and present data. Usually web based, desktop client versions available.
- Allows simple ad-hoc reporting capability of the DW instead of pre-canned reports.
- Allow the ability to create dynamic dashboards and score cards.
- Advanced report distribution and scheduling capabilities.
- Ability to cache reports avoiding unnecessary trips to the DW database.
- Built in Security model
BI tools generally read data that has been previously stored, often, though not necessarily, in a data warehouse or data mart type database.
Looking for assistance in your Data Warehouse project using Oracle technologies? Contact Us.
Alabra Consulting with over 10 years experience developing ETL routines for the Oracle DBMS.
